
In RStudio, removal, and undo’ing the removal, are simpler. This frequently causes panic in new git users when they don’t see the deleted file restored after running git reset.
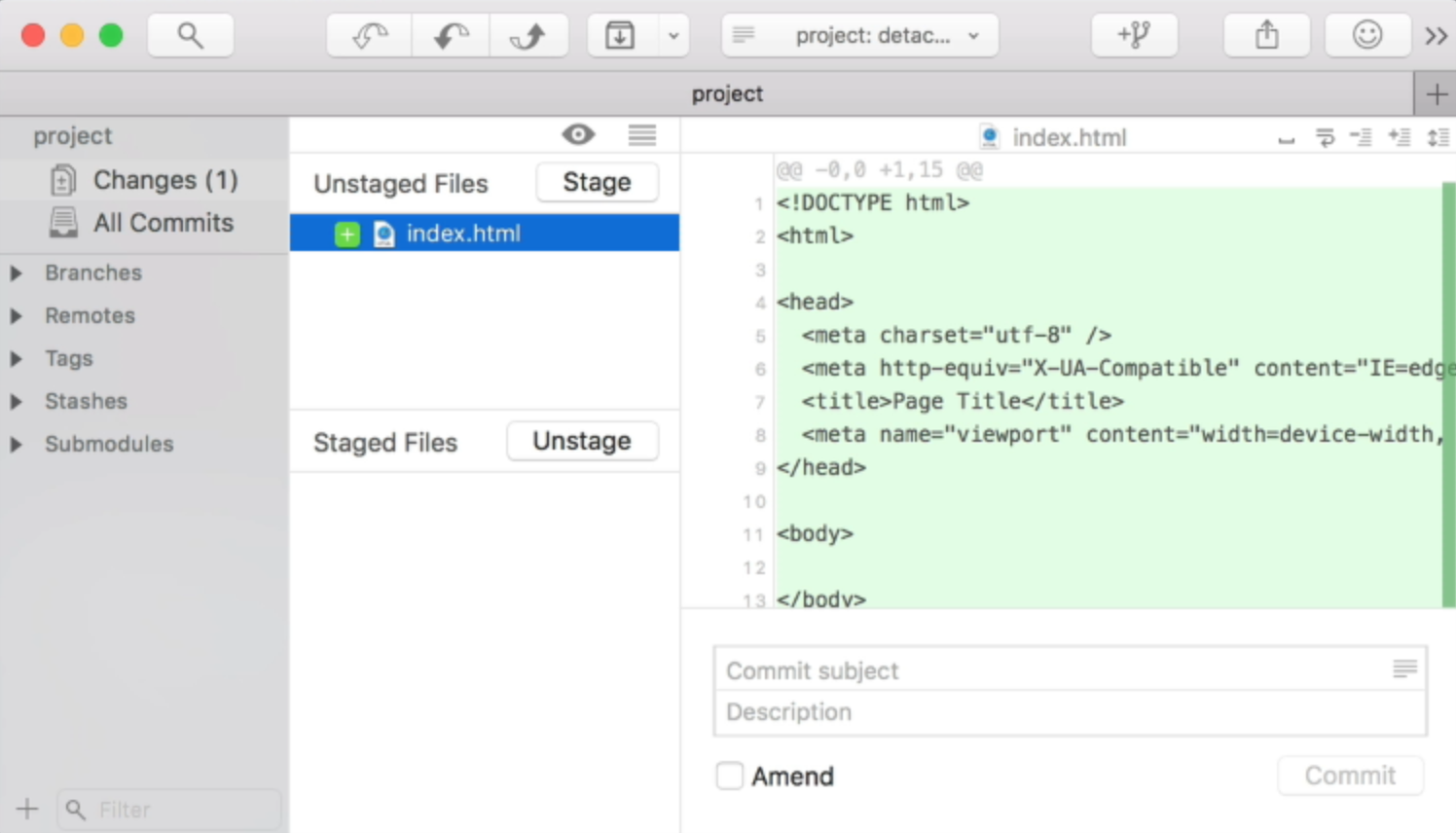
You cannot simply undo a git rm removal by running git reset - as we did with git add git rm stages the removal of the file so that the next commit knows the file was removed, but it also removes the actual file. Staging the removal of a tracked file looks simple, but be warned: Unstage a file with git reset, or in RStudio, just uncheck the checkbox. The green “A” icon is for Added (as opposed to a blue “M” for Modified, or a yellow “?” for an un-tracked file). In the above example, we have staged two files. In RStudio we can easily git add both types of changes to the staging area by clicking on the checkbox in the “Staged” column next to the filename:
add new changes to a previously-committed file. We use git add to add changes to the staging area. staged: changes that will be included in the next commit. unstaged: changes that won’t be included in the next commit. The changes to files in your project can be in one of two states: Git is used to keep track of how files change. To use git with an existing project, click on Tools -> Project Options -> Git/SVN: If you create a new project, RStudio will give you the option to use Git with the project: There are many ways to treat your RStudio project as a git repository, or repo for short. These values will later show up in all commit and collaboration messages, so make sure they are appropriate for public visbility. git configīefore getting started with git, you should identify yourself with: git config -global user.name "" The following commands should eventually become so habitual that they take only seconds to complete. I encourage you to practice with both the command-line and the RStudio Git interface. Once you have set up Git, here are 10 commands and their RStudio GUI interface equivalents to get started using Git. Resources such as HappyGitWithR and provide detailed setup instructions and interactive tutorials. The RStudio IDE offers Git functionality via a convenient web-based interface (see the “Git” tab), as well as interaction with git via the command-line (via the “Console” tab, or via the “Git” tab’s “More”->“Shell” menu option). While the emphasis is often on collaboration, Git can also be very useful to the solo practitioner. Git and its online extensions like GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab are essential tools for data science. Roland Stevenson is a data scientist and consultant who may be reached on Linkedin.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
